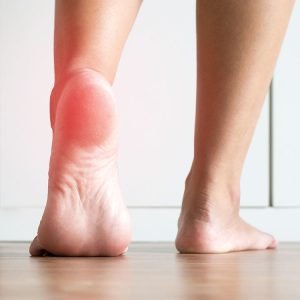
Joint instability occurs when the tissues surrounding a joint, such as muscles, ligaments, and bones, weaken and can no longer hold the joint in place. This can result in limited flexibility and weakened joints, making it difficult to perform daily activities. Joint instability most commonly occurs in unstable joints in the body such as the ankles, elbows, hips, knees, neck, shoulders, thumbs, and toes.
Understanding joint instability is crucial for those who experience it, as it can cause significant pain and affect their quality of life. There are various types of joint instability, including traumatic and atraumatic, and it can be caused by factors such as genetics, previous injuries, and overuse. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, stiffness, and a feeling of the joint “giving way.”
Key Takeaways
- Joint instability occurs when the tissues surrounding a joint weaken, resulting in limited flexibility and weakened joints.
- There are various types of joint instability, and it can be caused by factors such as genetics, previous injuries, and overuse.
- Symptoms can include pain, swelling, stiffness, and a feeling of the joint “giving way.”
Understanding Joint Instability
Joint instability is a condition where the tissues that hold the bones of a joint in place weaken, leading to limited flexibility and weakened joints. This condition most commonly occurs in unstable joints in the body such as ankles, elbows, hips, knees, neck, shoulders, thumbs, and toes.
There are several causes, including injuries, disorders, and genetic factors. Injuries that damage the joint structure or lead to joint instability are highly associated with osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease. Disorders such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Marfan syndrome, and Down syndrome can also cause joint instability.
Joint instability can be diagnosed through physical examination, X-rays, MRI scans, and arthroscopy. Treatment options depend on the severity of the condition and may include physical therapy, bracing, and surgery.
Physical therapy is often the first line of treatment for joint instability. A physical therapist can help strengthen the muscles around the affected joint and improve joint stability. Bracing can also be used to support the joint and prevent further damage. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or reconstruct the damaged joint.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have joint instability. Ignoring the condition can lead to further joint damage and may increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis. By understanding joint instability and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Types of Joint Instability
Joint instability can be classified according to degree, direction, etiology, and chronicity. The most common types are:
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Instability
ACL instability is a common knee injury that occurs when the ACL is stretched or torn. This type of instability can be caused by sudden stops or changes in direction, direct blows to the knee, or hyperextension of the knee joint. Symptoms of ACL instability include pain, swelling, and a feeling of instability in the knee joint.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Instability
PCL instability is less common than ACL instability and occurs when the PCL is stretched or torn. This type of instability can be caused by a direct blow to the front of the knee or from a fall onto a bent knee. Symptoms of PCL instability include pain, swelling, and a feeling of instability in the knee joint.
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Instability
MCL instability occurs when the MCL is stretched or torn. This type of instability can be caused by a direct blow to the outside of the knee or from a twisting motion of the knee joint. Symptoms of MCL instability include pain, swelling, and a feeling of instability in the knee joint.
Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Instability
LCL instability occurs when the LCL is stretched or torn. This type of instability can be caused by a direct blow to the inside of the knee or from a twisting motion of the knee joint. Symptoms of LCL instability include pain, swelling, and a feeling of instability in the knee joint.
Multidirectional Instability
Multidirectional instability occurs when a joint is unstable in more than one direction. This type of instability can be caused by ligament laxity, joint hypermobility, or muscle weakness. Symptoms of multidirectional instability include pain, swelling, and a feeling of instability in the joint.
Overall, joint instability can cause significant pain and discomfort, and it is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have this condition.
Causes of Joint Instability
Joint instability occurs when the tissues that support the joint weaken, causing the bones to move out of place. This can lead to limited flexibility, pain, and weakness. There are several causes, including:
Injury
Joint instability can be caused by an injury, such as a fall or a sports injury. Injuries can cause dislocations of the joint or stretch or tear the ligaments. This can lead to joint instability, making the joint more prone to future injuries.
Degenerative Diseases
Degenerative diseases, such as osteoarthritis, can cause joint instability. Osteoarthritis is a condition that occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joint wears down over time. This can lead to joint instability, making the joint more prone to dislocation.
Congenital Conditions
Some people are born with congenital conditions that can cause joint instability. These conditions can include hip dysplasia, which is a condition where the hip joint is not formed correctly, or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which is a connective tissue disorder that can cause joint hypermobility.
It is important to note that joint instability can occur in any joint in the body, including the ankle, elbow, hip, knee, neck, shoulder, thumb, and toes. If you are experiencing symptoms, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Symptoms of Joint Instability
Joint instability is a condition where the surrounding structures of a joint fail to stabilize it, leading to abnormal movements and discomfort. It can occur in any joint, but it is more common in the knees, ankles, shoulders, and hips. Here are some common symptoms:
- Pain: Mild to severe pain in the affected joint. The pain may be dull, achy, or sharp, depending on the severity of the instability.
- Swelling: Swelling around the joint is another common symptom. The swelling may be mild or severe and can make the joint feel stiff and difficult to move.
- Stiffness: Can cause stiffness in the affected joint, making it difficult to move and perform daily activities.
- Weakness: Weakness in the affected joint is another common symptom. The weakness can be mild or severe and can make it difficult to perform activities that require strength, such as lifting or carrying heavy objects.
- Giving way: Can cause the affected joint to give way or buckle, leading to falls and injuries.
- Popping or clicking: Popping or clicking sounds in the affected joint are also common symptoms. These sounds can occur when the joint moves or when pressure is applied to it.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis Methods
Physical Examination
The diagnosis of joint instability is mainly based on physical examination. The clinician will evaluate the patient’s joint for signs of instability, such as abnormal movement, pain, and tenderness. The clinician will also assess the patient’s range of motion, strength, and stability. The examination will include a detailed assessment of the joint, including the ligaments, tendons, and muscles surrounding the joint. The clinician may also perform special tests to evaluate the joint’s stability.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) scans, may be used to confirm a diagnosis of joint instability. X-rays can show any bone abnormalities or fractures that may be contributing to the instability. MRI and CT scans can provide detailed images of the soft tissues, such as the ligaments, tendons, and muscles, and can help detect any tears or other damage that may be causing the instability.
In some cases, the clinician may use arthroscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure, to directly visualize the joint and assess its stability. During arthroscopy, a small camera is inserted into the joint, allowing the clinician to see inside and make a diagnosis.
Overall, diagnosis is based on a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. A thorough evaluation by a qualified clinician is essential to accurately diagnose joint instability and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options
Joint instability can be treated with a variety of options depending on the severity of the condition and the location of the joint. The most common treatments include physical therapy and surgery.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can be a highly effective treatment. A physical therapist can work with patients to develop a customized exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the affected joint. This can help to improve joint stability and reduce the risk of further injury.
In addition to exercise, physical therapists may also use other techniques such as manual therapy, massage, and stretching to help improve joint mobility and reduce pain. They may also recommend the use of braces or supports to help support the joint during activity.
Surgery
In cases where physical therapy is not effective, surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged joint and restore stability. The type of surgery recommended will depend on the location and severity of the joint instability.
Some common surgical procedures include ligament reconstruction, joint fusion, and joint replacement. These procedures can be highly effective in restoring joint stability and reducing pain.
It is important to note that surgery is not always necessary. In many cases, conservative treatments such as rest, anti-inflammatory medication, and the use of braces or supports may be sufficient to manage symptoms and improve joint stability. Patients should work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the best treatment approach for their individual needs.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing joint instability is crucial for reducing the risk of developing osteoarthritis (OA) and other joint-related disorders. Here are some strategies that can help prevent it:
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises can help improve the stability of the joints by building up the muscles around them. These exercises can help improve balance, flexibility, and range of motion, which are all important for maintaining joint stability. Some examples of exercises that can be done to strengthen the joints include:
- Squats
- Lunges
- Leg presses
- Calf raises
- Planks
- Side planks
- Glute bridges
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for reducing the risk of joint instability. Excess weight can put additional stress on the joints, which can lead to instability and other joint-related disorders. Losing weight through a healthy diet and regular exercise can help reduce the risk.
Injury Prevention
Preventing injuries is important for reducing the risk. Injuries to the joints can cause damage to the ligaments, tendons, and cartilage, which can lead to instability and other joint-related disorders. Here are some tips for preventing injuries:
- Warm up before exercising
- Wear proper footwear
- Use proper form when exercising
- Avoid overexertion
- Take breaks when needed
Joint Protection
Protecting the joints can help reduce the risk. Here are some tips for protecting the joints:
- Avoid repetitive motions that can cause stress on the joints
- Use proper posture when sitting and standing
- Use assistive devices when needed, such as braces or splints
- Avoid activities that cause pain or discomfort in the joints
By following these prevention strategies, individuals can reduce their risk of developing joint instability and other joint-related disorders.
Living with Joint Instability
Living with joint instability can be challenging, but there are ways to manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of injury. Here are some tips for living with joint instability:
Protect the Joint
One of the most important things to do when living with joint instability is to protect the joint from further damage. This can be done by avoiding activities that put too much stress on the joint or by using protective equipment such as braces or splints. It is also important to maintain a healthy weight to reduce the strain on the joint.
Strengthen the Muscles
Strengthening the muscles around the joint can help to improve stability and reduce the risk of injury. This can be done through exercises such as resistance training, yoga, or Pilates. It is important to work with a qualified professional, such as a physiotherapist, to develop an exercise plan that is safe and effective for the individual.
Use Assistive Devices
Assistive devices such as canes, crutches, or walkers can help to reduce the load on the joint and improve stability. These devices should be used as directed by a healthcare professional and fitted properly to ensure maximum benefit.
Manage Pain and Inflammation
Joint instability can be painful and may lead to inflammation. Pain and inflammation can be managed through the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or other pain medications. Ice and heat therapy can also be helpful in reducing pain and inflammation.
Seek Medical Attention
If joint instability is causing significant pain or interfering with daily activities, it is important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can assess the joint and recommend appropriate treatment options, such as physical therapy or surgery.
Living with joint instability can be challenging, but with proper management and care, it is possible to reduce the risk of injury and improve quality of life.